The world is a diverse place, and every species has its respective characteristics that aid them in its survival. Turkeys are one of the most loved game birds in the United States and one of the toughest. Turkey hunting season has just bid us goodbye, and we are sure many young, passionate hunters returned with utter disappointment.
Let me tell you, a turkey’s eyesight is one of the best among many animals in the wild. They can spot you from afar and simply evaporate your dream of having a good game. People new to the Turkey hunting sport often ask the question, How do Turkeys see the world, or What colors do Turkeys see? To clear the mist, we have come today with our article on this very topic, “What color do Turkeys see? Turkey Vision vs Human Vision.”
Turkeys have a colored vision and see almost every color from the visible spectrum. Their vision even extends to ultraviolet light (UV). Apart from primary colors, they can also see various color shades and color combinations, thus heightening their color vision.
Later in this article, on What colors can Turkey see, we are going to explore every intricate detail of their eyesight. So without much ado, let’s dive into our today’s article.
What colors can Turkeys see? (Are Turkeys colorblind)
Turkeys have excellent color vision. They perceive a broad spectrum of colors, making their color vision much better than humans. Turkeys can see red, green, and blue colors from the visible spectrum and their shades and combinations. This amounts to nearly thousands of colors that a turkey can see.
To answer the second question, No, Turkeys are not color blind. They possess excellent color vision and can perceive almost every color from the visible spectrum. Their vision extends to practically all hues from the visible light spectrum and is therefore not color blind towards any color.
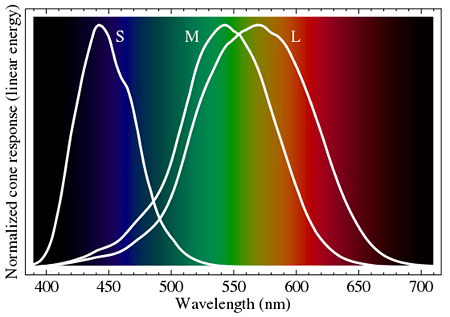
Retinal cells play a significant role in the vision of a species. Every species on earth have its respective number of cells, which are of two types: rods and cones. Cone cells play a significant role in colored light perception, as they possess the visual pigment responsible for colored vision.
Turkeys have 6 different types of cone cells- two double cones and four single cones. These cone cells are, Long wavelength sensitive (LWS) (564 nm), Medium wavelength sensitive (MWS) (505 nm), Short-wavelength sensitive (SWS)(460 nm), Violet sensitive (VS)(420 nm), and even Ultra-violet sensitive (400 nm).
The short-wavelength sensitive cones help to detect colors on the blue side of the visible spectrum like Indigo, Blue, etc. The Medium wavelength sensitive cones allow the animal to perceive colors like Yellow, green, and its shades.
The Long-wavelength sensitive cones give Turkey’s vision the ability to perceive red color and its multiple shades. Even fluorescent colors and near-ultraviolet colors are also exceptionally well perceived by Turkeys.
What colors can Turkeys not see?
Turkeys’ color vision is one of the best in the world. Their color vision extends to almost all colors of the visible spectrum. Turkey’s vision allows them to see nearly thousands of color combinations and shades. So, there are no colors a Turkey cannot see.

Turkeys have 6 cones that provide them with extensive color vision. While three cones respond to short, medium, and long wavelengths, respectively, the fourth cone perceives
Ultraviolet Light, and the other two as double cones. From Ultraviolet to Red, almost all colors that occur from these color combinations are well perceived by Turkeys.
However, they do not have any vision for wavelengths that lie beyond Red (625-650 nm). Since Turkeys are warm-blooded animals, their bodies release heat.
Therefore, it is scientifically not possible for Turkeys to perceive Infrared radiation. This is because Infrared or Near Infrared light has large wavelengths and lesser photon energy.
This low energy does not stimulate opsin visual pigment in the cones as they have a higher energy barrier. For opsin to detect Infrared, the energy barrier needs to be lowered, which will make the entire mechanism for vision pointless.
Turkeys also lack a definite 3D vision and are almost non-existent in them. For this very reason, hunters wear 3D outfits with leafy patterns to camouflage with the environment around them.
Can Turkeys See in the Dark?
No, Turkey’s vision does not provide the ability to see in the dark. Though not utterly blind at night, their night vision is extremely feeble. Turkey’s highly heightened daylight vision takes up the space for their night vision.
Among the two types of retinal cells responsible for vision, it is the Rod cells that take up the role for low light vision. Turkeys have 7 photoreceptor cells, 1-rod cell, and 6 cone cells. Rod cells have the visual pigment Rhodopsin. For good vision in low light or at night, it is essential to have abundant rod cells.
Owls, which have poor day vision and heightened night vision, have an abundant number of rod cells than cones. Turkeys have 6 cone cells and therefore have an excellent daytime vision and color perception.
On the other hand, the number of rod cells is only 1. This dramatically limits their night vision and also vision in low-light conditions. The presence of a rod cell prevents them from getting completely blind at night. This can be cited as an evolutionary feature, where the night vision has been somewhere sacrificed for heightened daytime and color vision.
How far can Turkeys see?
Turkeys can see clearly up to 3 miles or even greater, provided the vision is unhindered. They can see nearly 3-4 times better than humans and almost 8 times farther. They are excellent in motion sensing and can detect movements exceptionally well, much better than we humans can imagine.
Turkeys have high visual acuity. In comparison to humans with a vision of 20/20, Turkeys have a vision of 60/20. This implies that they can see objects at 60 yards what we humans see at 20.
If the eyesight is unhindered, Turkeys can easily see up to 3-4 miles. They can pick up movements with utmost precision, no matter how slow or fast they may be, even from great distances.
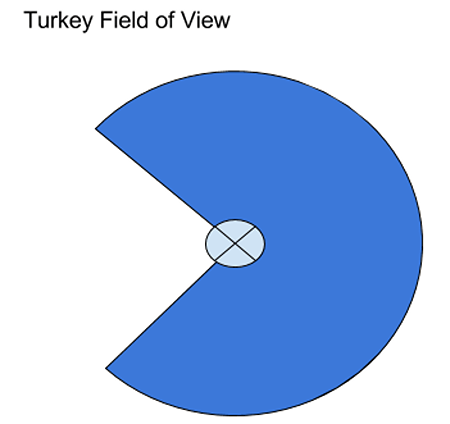

Apart from this, Turkeys also enjoy a large field of peripheral vision, nearly 270 degrees. Their farsightedness, coupled with their peripheral field makes no object invisible from their sight.
Next up in our article, “What colors can Turkeys see?”, we are going to dig deep into their eyesight. So, let’s get to it without much ado.
How Good is Turkey’s Eyesight?
Turkeys have excellent vision. They can perceive almost every color and their shades and combinations from the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Let us dig deep into the segment below and unveil more secrets about Turkey’s eyesight.
Turkeys have 6 cone cells that provide them extensive color vision. They are even capable of perceiving UV light. This ability places hunters in quite a problematic situation.
Often their camos are washed with detergents that, even after a wash, emit Ultraviolet light. Turkeys quickly perceive these transmitted UV lights, and they become alert to the hunter’s presence.
Even urinating around tree bases is visible in UV, further alerting the birds about an external presence. Their UV vision helps them to search for prey and also to spot and escape from predators.
Turkeys have their eyes on the sides of their heads. This provides them with monocular vision, which is further periscopic. The location of their eyes gives them a sizeable peripheral vision, of nearly 270 degrees of field view. Turning their heads sideways, they can easily achieve about 360 degrees of field view.
However, this also comes with certain disadvantages. The sidewise position of their eyes gives them monocular vision, causing significantly less field overlapping. This causes poor 3D perception and is almost non-existent in Turkeys.
Hence, despite being adept at color vision, their depth perception is not quite developed. Turkeys make up for this by bobbing their heads to gather information regarding objects’ relative depths and measuring distances.
Turkeys are excellent in motion sensing, thanks to their rod cells. They can quickly pick up and analyze movements, no matter how slow or swift they may be, much faster than humans. Hunters need to be highly patient and restrict their movements to the least, as it might further reduce their chances of getting a game.
Turkey’s response to various colors
Q1. Can Turkeys see Orange?
Ans– Yes, Turkeys can see Orange color. Orange is a color formed by the combination of yellow and red. According to Physics, Orange color has its wavelength in the range of 580 – 600 nm.
Among the 6 cone cells present, one cone is Long-wavelength sensitive that perceives colors like red and yellow. It is this cone that provides Turkeys the ability to see Orange color.
Q2. Can Turkeys see Green light?
Ans- Yes, Turkeys can see Green light too. Green light, in the visible spectrum, lies between Blue and Orange and is formed by the combination of these two lights.
As a result, green light has its wavelength in the range of 520 – 560 nm and falls in the category of medium wavelengths. Turkey’s retinal cells have a Medium Wavelength Sensitive cone for the perception of colors like green and its vast catalog of shades.
Greenlight perception is extremely important for prey animals, like Turkeys, especially in the wild. It helps them to track even predators’ activities with precision and escape from them.
Q2. Can Turkeys see Red Light?
Ans- Yes, Turkey can see Red Light too. Red light lies at the end of the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. It has the longest wavelength among all visible lights (625 nm and above).
The 6 retinal cones of a Turkey also have a Long Wavelength Sensitive cone for the perception of wavelengths like yellow, orange, and Red. The energy threshold of the LWS cone is nearly 600 nm.
Therefore, though they can see Red light well, it is not perceived with that much acuity like colors on the other end of the spectrum, like Blue, Violet, green, etc.
The spectacular vision of Turkey is best at low wavelengths, and as it goes higher, it drops slightly in its strength. Beyond Red lies Infrared light, which has no perception mechanism in Turkeys like other warm-blooded animals.
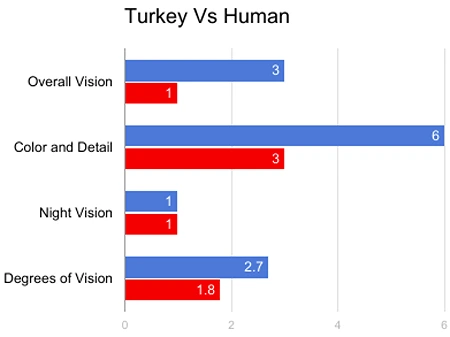
Turkey’s Vision vs Human Vision
| Turkey vision | Human vision |
| 1. They have 6 cones in their retina. | 1. Humans have 3 cone cells in their retinas. |
| 2. Only one-rod cell help in Turkey’s vision. | 2. They too have rod cells. |
| 3. Turkeys can see objects under Ultraviolet light, i.e., they have ultraviolet vision. They can also perceive near-Ultraviolet colors. | 3. Humans cannot see or perceive Ultraviolet light, as they are blocked from entering the eye by the intraocular lenses. |
| 4. Infrared Vision or Near Infrared (NIR) is absent in Turkeys. | Humans, too, do not have any Infrared Vision. |
| 5. Vision is monocular. | 6. They enjoy binocular vision. |
| 6. Turkeys have nearly 270 degrees of field view under peripheral vision. | 6. Humans have a field view of nearly 180 degrees. |
| 7. Poor depth perception. | 7. They have extremely well-developed depth perception. |
| 8. Turkeys have a visual acuity of nearly 60/20. | 8.The visual acuity score for humans is nearly 20/20. |
| 9. 3D perception in Turkeys is quite poor and is almost non-existent. | 9. The 3D perception in humans is quite well developed, as they have binocular vision. |
Here we come to the end of our article, “What colors can Turkeys see? Turkey’s Vision vs Human Vision” Hope the article has given you enough information about Turkey’s eyesight and vision. Next time you go for a game, make sure to take all precautions to escape from their laser like vision. We will be returning soon with another informative post. Until then, you can glance over articles on several other niches.
Also Read:

Meet Abhidept (nickname Monty), the visionary founder of How It See, being an engineering student, he’s fueled by an insatiable curiosity about the world around him. He is captivated by an eclectic correlation between animal groups, science, and nature, and this fascination drives his quest for understanding.
After completing his degree, he’s set on a mission to delve deep into the realm of nature, accumulating knowledge to share with you through his writing. In the meantime, he loves to watch anime and read anime.

Comments are closed.