Dolphins are the aquatic mammals that belong to the families that are Delphinidae, Platanistidae, Iniidae Pontoporiidae, and the extinct Lipotidae, depending on the region.
According to various mythologies, Dolphins played a significant role in human culture. And in the present scenario, they are good friends of ours. So, have you ever been fascinated by how dolphins see the world or what colors they see? If yes, then below is the answer.
Dolphins have very good eyesight, and they primarily rely on their well-developed sense of vision to see underwater and on land. They are monochromats, meaning they have only one kind of cone in their retina, allowing them to distinguish the world in black and white hues.
On the other hand, humans are trichromats and have three special cones sensitive to blue, green, and red. Hence, we are able to distinguish millions of color shades ranging from 380 nm to 720 nm wavelength.
However, dolphins do not need color-eyesight. They have excellent vision and a sonar-like system called Echolocation that helps them process the visual information deep inside water over a large range. With this ability, they can sense their environment underwater much better than any other marine life.
Later in this article, we have explained Dolphin Vision in detail. So, without any further delay. Let’s begin.
Are Dolphins Blind?
Most dolphin species are not completely blind; however, their vision is primarily dependent on their species. Ocean dolphins have an excellent vision; however, river-dwelling dolphins that usually live in murky water have poor eyesight.
According to the WWF India, Gangetic Dolphins are primarily blind, and they use Echolocation to catch their prey and navigate their surroundings. They do not need the vision to survive in murky water; thus, they have developed advanced ways to capture their prey.
In addition, the South Asian River Dolphin has very poor eyesight that permits it to distinguish only the brightness of light and shapes. Due to lack of vision, river dolphins rely on their Echolocation, where they emit an ultrasonic to detect which reaches the prey.
In contrast, most dolphins live in the clear ocean, where eyesight plays a significant role. Therefore, they have evolved their eyesight to see both in water and on land. Dolphins have lenses and the cornea in their eyes that adjust with the help of special muscles accordingly to the refraction of light underwater and on land.
Also, dolphins are not near-sighted even in the water. Their eyes comprise both rods and cones that assist them in witnessing underwater even in the slightest of light.
Even though ocean dolphins have good vision, they primarily use their sonar system to sense long distant movements. It is estimated that they can perceive an entity the size of an orange from over eighty meters away using their Echolocation.
How Echolocation works-
Echolocation, also called biosonar, works the same as the sonar system. Dolphins emit a series of sound waves through the melon (forehead as demonstrated in the image).
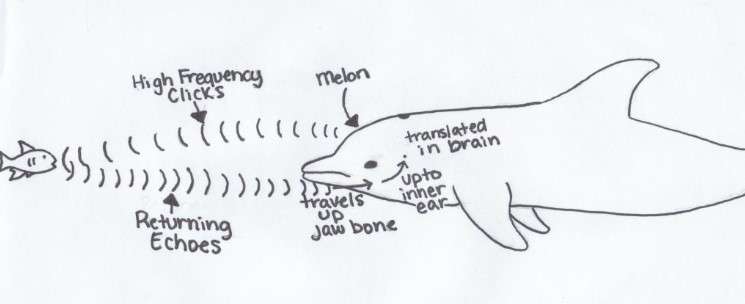
Credits: Mandurah Cruises
The high-frequency sound pulse or clicks travels, and if an object is in the path of the sound pulse, the sound bounces off the object and returns an “echo.” These returning echoes are picked up from the lower jaw of the dolphins and then conducted to the inner ear.
Based on these echoes, dolphins can determine the shape, size, speed, distance, density, and direction of the object and form a picture of it. These various images are saved in their memory, and they instantly recognize whether the object is a fish, shark, reef, boat, human, etc.
About Dolphins’ eyes-
Dolphins’ eyes can move independently of each other in any direction, allowing them to see in two directions at one time. They have 300 degrees of panoramic vision, covering a large range of vision.
With this panoramic vision, they are able to notice forward, backward, and to the sides but not upward. It assists them in avoiding predators and chase prey.
Can Dolphins see colors, or are they colorblind?
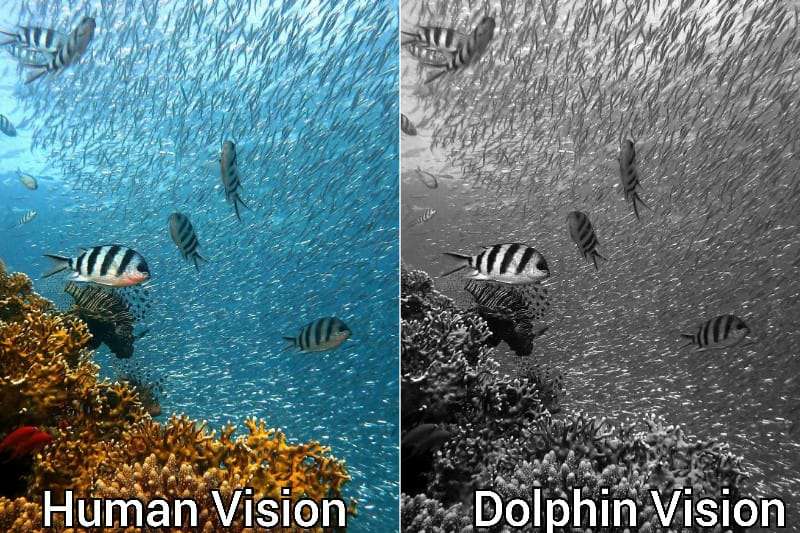
Dolphins are colorblind and see the world mostly in shades of gray. Like whales, Dolphins are monochromats. It means they have only one kind of cone in their eyes: L-cones that are sensitive to long-wavelength light.
Only with one cone, dolphins have limited color vision and poor visual acuity that assists them in recognizing only black and white hues. It is unlikely for any animal to distinguish between colors without the presence of at least two cones in the eyes.
Humans are trichromatic, meaning we have three different types of cones in the eyes that perceive blue, green, and red colors from wavelength 380 nm to 720 nm (visible spectrum). With the help of these cones, we are able to discern millions of color shades visually.
Additional information: Retina has two types of photoreceptors to gather light: rods and cones. Rods help to control the brightness of light, whereas cones assist in distinguishing the millions of colors.
Can Dolphins see in the dark?
Dolphins can see much better in the dark compared to humans. Like many nocturnal animals, dolphins have enlarged tapetum in their eyes. Tapetum lucidum is a membrane that reflects even the slightest of light back to the retina.
It provides dolphins with better night vision. Along with it, the dolphin’s eye has 7,000 times as many rod cells compared to the human eye allowing it to see much better in low-light conditions.
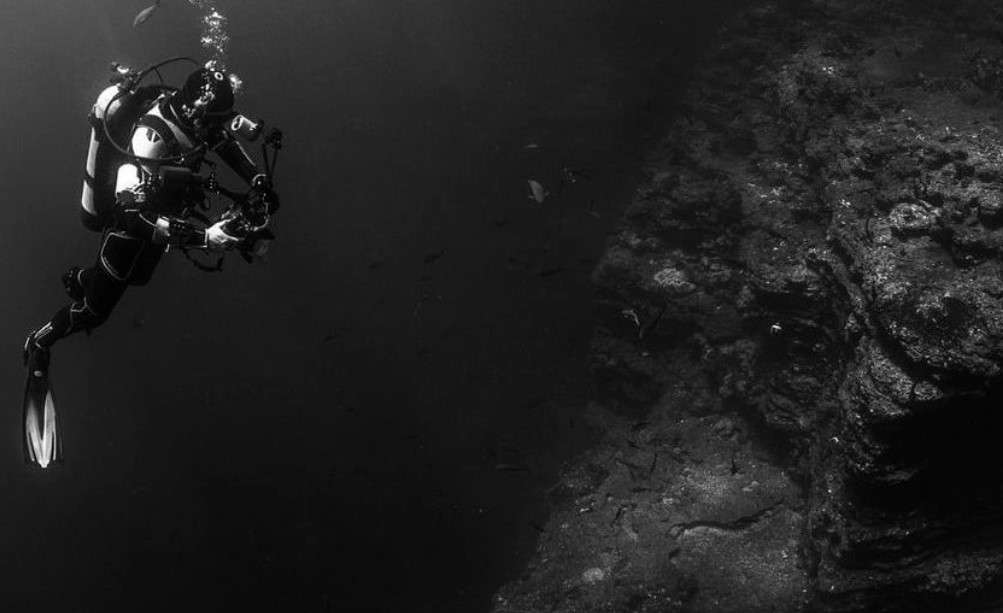

The human eye is more concentrated on cones, whereas the dolphin eye has more rods. Therefore, in exchange for color vision, they have gained superiority in night vision.
Not only this, to visualize the environment in complete darkness, dolphins use Echolocation, which makes them better than any other mammals.
Do Dolphins have good eyesight?
Most dolphins have very good eyesight compared to other underwater mammals. However, their vision primarily relies on their habitats. For example, river dolphins have poor visual acuity, whereas ocean dolphins have excellent eyesight.
Along with their vision, they use a sonar-like system called Echolocation to track their prey and apprehend their surroundings. In this way, river dolphins are not dependent on their eyesight.
How do Dolphins see Humans?
Dolphins can see and recognize humans. They even categorized us differently from other animals. Many dolphins are friendly to humans, and some species are noted for seeking out social encounters with us.

Dolphins have well-developed brains and emotional intelligence. Also, they have compassion and empathy for humans like dogs because they distinguish us as intelligent creatures like them.
But not all dolphins are friendly. Remember, they are wild sea creatures, and sometimes they show non-friendly behavior. Dolphins can be as dangerous as sharks if they feel threatened.
Dolphin Vision vs Human Vision
| Dolphin Vision | Human Vision |
| Dolphins have monochromatic vision | Humans have trichromatic vision |
| They are colorblind. | We can see millions of color shades. |
| Dolphins have excellent night vision. | Humans do not have night vision. |
| They can use bio-sonar to recognize their surroundings. | We can use our eyes to visually glimpse our surroundings. |
Here, we conclude our article on “What colors do Dolphins see,” along with the explanation of dolphin’s vision in detail. We hope you like this post. We will be back with another article. Till then, stay tuned with us and read the articles below.
References:
How Dolphins See The World Compared To Humans by Business Insider
Also Read:

Meet Monty, the visionary founder of How It See, being an engineering student, he’s fueled by an insatiable curiosity about the world around him. He is captivated by an eclectic correlation between animal groups, science, and nature, and this fascination drives his quest for understanding.
After completing his degree, he’s set on a mission to delve deep into the realm of nature, accumulating knowledge to share with you through his writing. In the meantime, he loves to watch anime and read anime.

