Tigers, a member of the genus Panthera, are the immense living cat species initially discovered in 1758. Since then, it has been on various headlines due to the exponentially declining of their population.
But after too much strict regulation, Tigers’ population slightly increase from extinction. So, back to the science, have you ever wondered how Tigers see the world, or can Tigers see in the dark? If yes, let’s read.
The answer to the question, “Can Tigers see in the dark,” is: Tigers can see up to seven times better than humans in the dark with the help of a large number of rods and tapetum lucidum in their eyes. Their eyes evolved to perceive the environment far better than us at night.
Tigers have a vision that focuses more on brightness rather than the colors. It means they have great night vision but cannot glimpse the colorful world like humans.
Later in this post, we have discussed much of the tiger’s vision in detail. So, without any further ado, let’s begin.
Note- This article is only for knowledge-sharing purposes
Can Tigers see in the Dark?
Tigers have a great night vision and can see exceptionally well in the dark. Like other nocturnal predators, tigers have a good rod density in their eyes that allows them to perceive even the slightest amount of light.
And they also have a thin reflective membrane behind the retina called tapetum lucidum that enhances the visual sensitivity in low-light conditions with the help of the light-sensitive retinal cells. In this way, they can witness the surroundings brighter than us.

However, tigers and other nocturnal animals cannot see in the total darkness. There should be a minimum moonlight to witness the surroundings and movements.
Tigers are mostly active at night, and to sneak up on their prey, they should need great night vision. For this, they have forward-facing eyes with wide and round pupils that provide binocular vision.
It indicates they can create three-dimensional images with distance accuracy and great depth.
Also, their retinas comprise predominately rods that are sensitive to minimal light conditions. Therefore, the combination of night and binocular vision grants tigers the proficiency to sense the slightest movements in the dark.
But tigers’ vision is only limited to the movements. It signifies they undergo tremendous difficulty in identifying stationary objects in the dark.
Not only tigers, mostly cat species, have a wide horizontal line of nerve cells near the eye’s center that enables them to have a better peripheral vision. It also helps them to concentrate on their running prey.
Can Tigers see color?
Tigers can see colors mostly in blue, green, and gray shades. They have a dichromatic vision, which means the rods and cones in their eyes are only sensitive to low and middle wavelengths (blue-green shades) ranging from 421 nm to 558 nm at best.
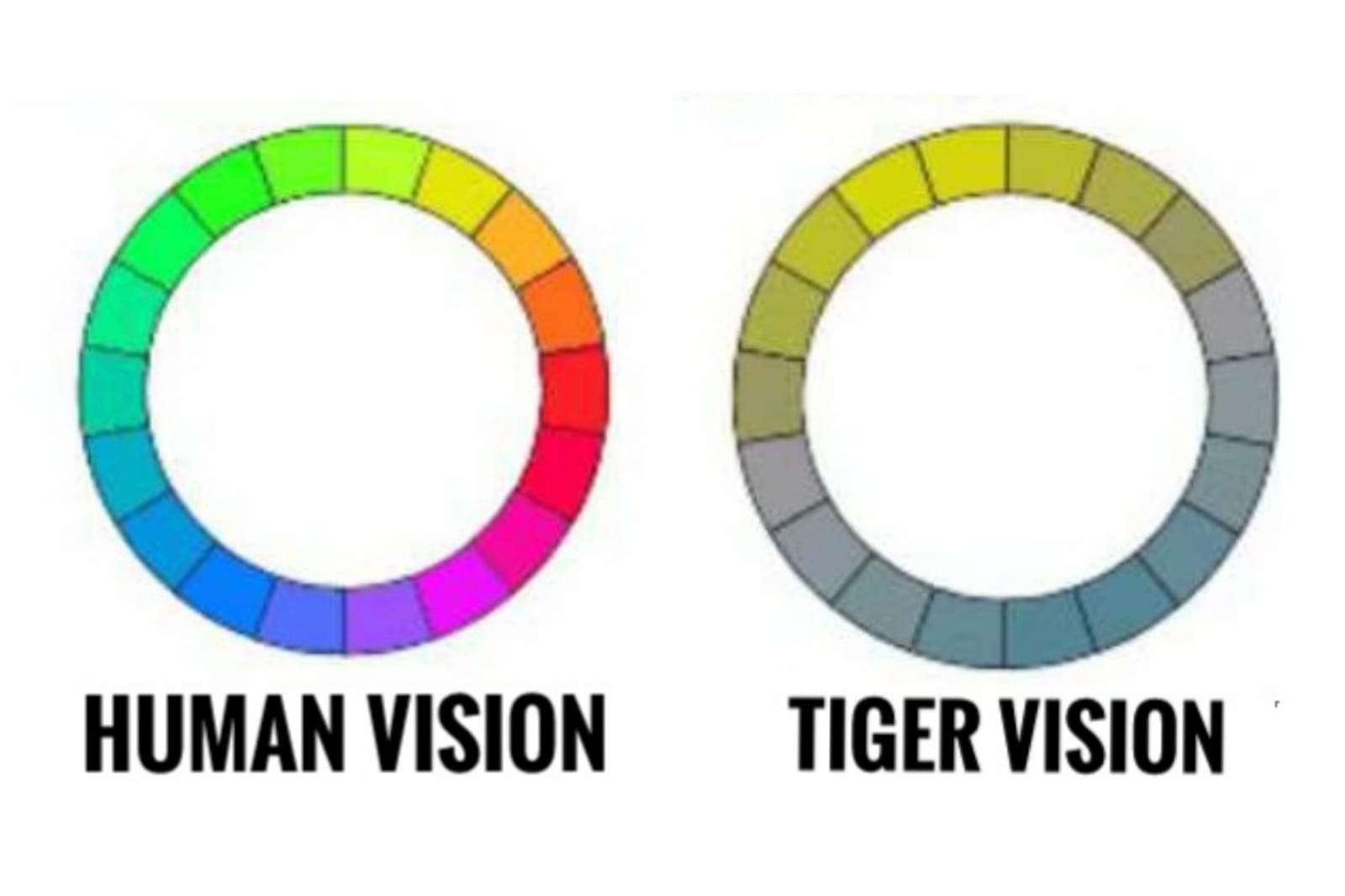
On the other hand, humans have trichromatic vision, which implies our cones receive the light from the wavelength of 380 nm to about 750 nm and distinguish in the form of blue, green, and red shades.
Unlike humans, tigers cannot glimpse millions of color shades. They witness the world in blue, yellowish-green, and grayish shades the most.
Being dichromatic means that tigers are able to distinguish between blue shades from the green but find difficulty in differentiating red from green or orange. They discern all shades of red in brownish-gray.
Tigers’ eyes have more rods density that dominantly focuses on brightness, but their eyes have some cones too that react with various colors.
Also, it is assumed by some researchers that tigers may sense red too in dull shades. However, it is not proven yet.
Tigers are also near-sighted like other cat species. However, they mainly depend on their smell and other senses to survive in the forest. Many forest animals, whether it is a deer or a tiger, have red-green color blindness.
Their color vision is limited to small and medium wavelength color shades. But they are sensitive to black and white colors that allow them to survive in the dark.
Are Tigers Colorblind?
Tigers are not completely colorblind; they can perceive colors but cannot distinguish them in millions of shades as humans do. They lack large wavelength cones in their retinas, making them red-green colorblindness.
In the past, it was believed that tigers were colorblind, but recent research proves that tigers can see colors mainly in blue, yellow, and gray shades. The structure of their eyes is more concentrated on the depth rather than the color.
It gives them the advantage of discerning the slightest movements, clear visibility, and distance measurements.
The human eye has more cones that qualify us to recognize millions of color variations but cannot discern things in the dark.
Do Tigers have Good Eyesight?
Yes, tigers have good eyesight, the same as humans, but the dissimilarity depends on their visual acuity and color differentiation. Their eyes have a large anterior chamber, and a wider pupil provides them good eyesight in the dark.

As justified by the recent study, tigers have some cones in each retina, indicating that they have some color vision that supports them to see in the daylight with colors.
Tigers also have nictitating membranes; the third eyelid constantly removes dust from the cornea and keeps it moist. It assists them in maintaining good eyesight over a while.
How do Tigers see the world?
Tigers see the world primarily in blue, yellow, and gray shades with clarity up to 20 feet in daylight. They are near-sighted and notice the far objects in dull.
They are dichromats, unlike humans, and have the large wavelength cone missing in their eyes. That’s why they are unable to perceive the large wavelength colors like the shades of red and orange.
However, in exchange for cones, they have more rods in their eyes compared to humans assists them in seeing much better in low light conditions.
There are two types of photoreceptors in the retina: cones and rods.
Cones are responsible for color vision, and rods help to sense the light. In the cones, humans have the upper hand; that’s why we can see millions of color shades.
But in rods, tigers can easily surpass us.
At night, tigers catch sight of its surrounding with the help of tapetum lucidum. And in the full moon night, they spot everything as bright as day with white and black shades.
Below we have inserted the pictorial representation of how well tigers see the world in both day and night.
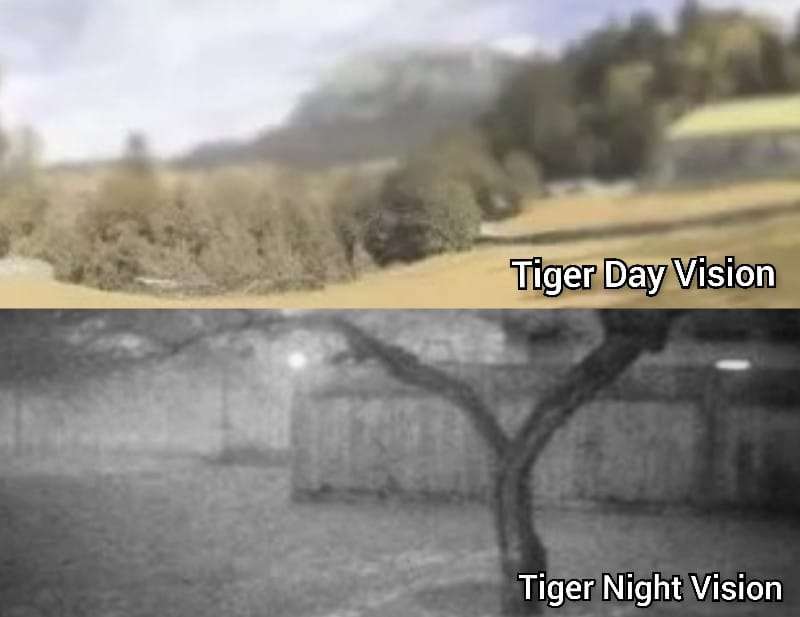

As justified in the image, tigers see the world much similar to most wolves. To read more about wolves, visit the article underneath.
Must Read- What colors do Wolves see?
Tiger vision vs Human vision
| Tiger Vision | Human Vision |
| Tigers are dichromats. | Humans are trichromats. |
| They have blue-green sensitive cones. | We have blue, green, red sensitive cones. |
| Tigers can see the world mostly in blue, gray and yellowish shades. | Humans can see the world in millions of color shades. |
| They have excellent night vision. | Humans do not have night vision. |
| Tigers can see clearly up to 20 feet. | We can see up to 3 miles. |
Here, we conclude our article on “Can Tigers see in the dark,” along with other relevant questions on Tigers’ Vision. We hope you enjoy reading this post. We will be back with another post. Till then, stay tuned with us and read the articles below.
Frequently Asked Questions-
Q1. Why do Tigers attack humans?
Ans. Tigers generally attack humans when they are trespassing in their territory or due to hunger.
Q2. How far can a Tiger see?
Ans. Tigers are narrow-sighted and can see clearly up to 6 meters.
Symbols-
nm- nanometer
1 nm = 10-9 meter
References-
Tiger Eyesight by Seaworld
Optimizing color by Journal of Royal Society Interface.
Also Read:

Meet Abhidept (nickname Monty), the visionary founder of How It See, being an engineering student, he’s fueled by an insatiable curiosity about the world around him. He is captivated by an eclectic correlation between animal groups, science, and nature, and this fascination drives his quest for understanding.
After completing his degree, he’s set on a mission to delve deep into the realm of nature, accumulating knowledge to share with you through his writing. In the meantime, he loves to watch anime and read anime.
