Humans have come to know a lot about the secrets of this living world, and there is a lot more to come. And the most interesting thing that amazes me about these creatures is their eating habits. This extremotroph wiki article will tell you a lot.
The animals I will be talking about in this essay are so amazing that they eat things most living things do not even think of as food. Introducing the species that is extremotrophic.
Here are some examples of such species. So let’s get started.
What Are Extremotroph Species?
Firstly, it is important for us to identify these extremotrophic species. Let’s start with the meaning of this word. Thus, the term “extremotroph” is a compound of the words “troph,” which means food, and “extremus,” which implies extreme.
Extremotrophs are a group of organisms that feed on matter that is not even considered food by other living organisms.
These creatures are used as bioremediation agents. But the question is how they are adapted in such a way. It’s still under research.
List of Extremotroph Species
1. Plastic-eating mushrooms
- Scientific name: Pestalotiopsis microspora
- Feed on: Plastic (Polyurethane)
This particular fungus has a unique capacity to degrade and break down polyurethane.
Polyurethane is basically an artificial polymer that is used in the formation of plastics, foams, etc. Researchers employ these endophytic fungi’s capacity in certain processes, like waste management and bioremediation procedures.
Are these still safe to eat, in your opinion? According to some studies, eating these mushrooms can be hazardous since they can occasionally become poisonous due to the excessive absorption of toxins in mycelium.
2. Halomonas titanicae
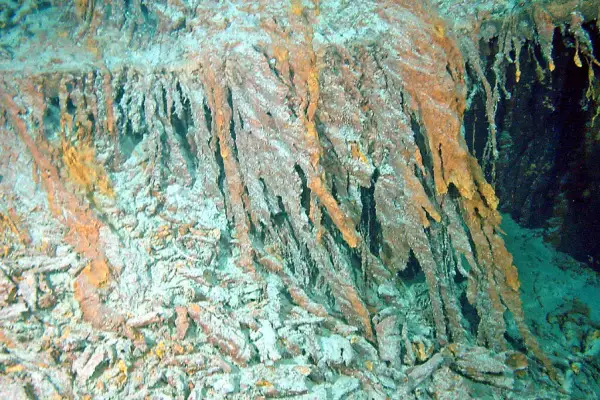

- Scientific name: Halomonas titanicae
- Feed on: Metals
Halomonas titanicae is an extremophile that has the ability to survive in extreme salt concentrations. They are named titanicae as they were first found on the wreck of the Titanic.
Let’s get more into the details of this bacteria. They have one flagella that helps with motility, are rod-shaped, and are gram-negative.
You must be wondering why I included this bacteria in this list. Let me explain.
3. Geotrichum candidum
- Scientific name: Geotrichum candidum
- Feed on: Metal, Polycarbonate
Do you know anything about geotrichosis? Indeed, it is an uncommon fungal illness that frequently affects people living with HIV/AIDS. We will not discuss this sickness; rather, we will concentrate more on the agent that causes it.
Geotrichum candidum, which is the major part of the human microbiome, is primarily associated with skin, sputum, and feces.
Depending on their surroundings, these bacteria have different eating behaviors. Their main source of food is iron and other metals, which they corrode.
Research indicates that they have the ability to break down the polycarbonate, which makes up the majority of the plastic layer of CDs, and harm the data contained therein.
4. Acidithiobacillus
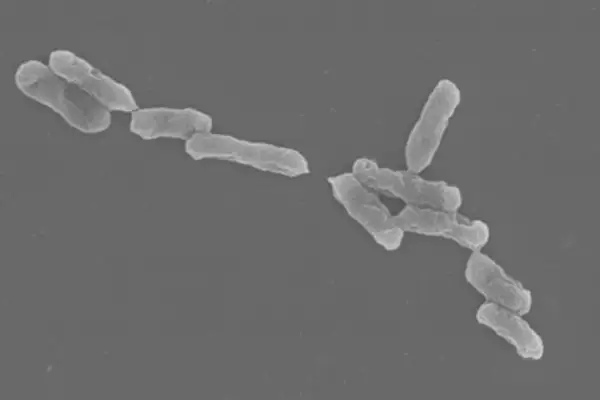
- Genus: Acidithiobacillus
- Feed on: Sulfur compounds, metals
Another extremophile we have on our list of extremotroph species is Acidithiobacillus bacteria. These groups of bacteria are rod-shaped, gram-negative, and non-sporing and they have a special ability to thrive in acidic conditions.
These organisms play a crucial role in the biomining and bioremediation processes because of their capacity to oxidize metals and sulfur.
These bacteria use sulfur and metals as energy sources. Their ability to use sulfur compounds as energy sources helps them survive in low pH environments like 1 or 2.
In areas with low pH, they are also crucial to biogeochemical cycles. These days, industries also use them in the bioleaching process.
These qualities make them extremely significant creatures in a variety of ways.
5. Deinococcus radiodurans
- Scientific name: Deinococcus radiodurans
- Feed on: Radioactive waste
Introducing Dienococcus radiodurans, a renowned species in the scientific community. These bacteria possess a rare and exceptional capacity to endure in a variety of harsh environments, including acid, vacuum, dehydration, and freezing.
According to the Guinness Book of World Records, they are the toughest bacteria on earth. these large, spherical and gram-positive bacteria, which can withstand a high level of radiation.
They have the ability to oxidize these radioactive elements so easily and are not known to cause any disease in humans.
These fascinating bacteria have been employed by researchers for bioremediation because of their ease of use in clearing radioactive, heavy metal, and toxic solvent-contaminated soils.
These days, they have also become a major part of nanotechnology, which is used in the production of silver and gold.
6. Actinobacteria
- Phylum: Actinomyces
- Feed on: Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
You must have heard about Actinobacteria once. Perhaps you are unaware of them monetarily, but not physiologically. Their capacity to break down plant or animal detritus is one of their key functions in soil systems. Let’s talk about their composition.
They are gram-positive, rod-shaped, facultative anaerobic bacteria that form endospores.
These bacterial communities aid in the bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), providing a viable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly substitute for conventional physicochemical methods for removing diffusive contamination of persistent organic pollutants in a range of settings.
In humans, they cause actinomycosis, which is identified by lumps and hard masses that may contain pus, which is treated by using the antibiotics penicillin or amoxicillin.
Conclusion
With this, we come to our end. This article is about the extremotroph species, which not only have the ability to eat anything but can also thrive in extreme conditions.
In various processes, such as bioremediation, bioleaching, biomining, the production of dairy products like cheese, yogurt, etc., and waste management, humans are now using these species, as you can see above.
Hopefully, this Extremotroph Wiki article will help you learn more about these amazing creatures. Enjoy this one till we next write together, which will be in the following piece.
Also Read:

Being a zoology student I’m always been fascinated toward animals especially insects. I love to do research and learn about different animals. As a writer I want to share my thoughts about nature through my articles. Apart from this you can find me exploring the new places and voice notes.
