Nature is full of surprises, but it can also be extremely deadly. There are many creatures on the planet that are exceedingly poisonous and can kill people. These species are not to be trifled with, from microscopic insects to enormous beasts. In this article, we will look at the 22 most poisonous animals under the sea, which you should never touch or eat. We’ll look at the science underlying their poison, habitats, and hunting strategies. So buckle up and prepare to learn about some of the world’s deadliest beasts.
22 Most Poisonous Animals Worldwide
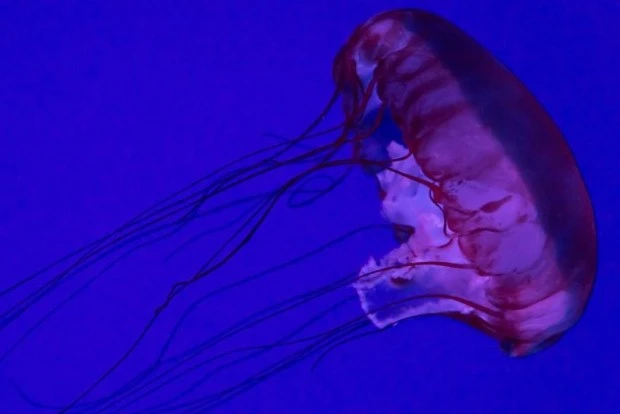
1. Box Jellyfish

| Scientific Name | Chironex fleckeri |
| Size | Up to 30 cm bell diameter, up to 3 m long tentacles |
| Habitat | Coastal waters, estuaries |
| Location | Northern Australia, Southeast Asia, Pacific islands |
| Danger Level | Very dangerous, poisonous |
| Number of Deaths in a year | Estimated 20-40 deaths per year |
The medusa form of a box jellyfish gets its name from its squarish, box-like bell. A short pedalium or stalk hangs from each of the four bottom corners of this, bearing one or more long, slender, hollow tentacles.
When the bell pulsates, the rim of the bell folds inwards to form a shelf known as a velarium, which confines the aperture and creates a forceful jet. As a result, box jellyfish can travel faster than other jellyfish, reaching speeds of up to 6 meters per minute.
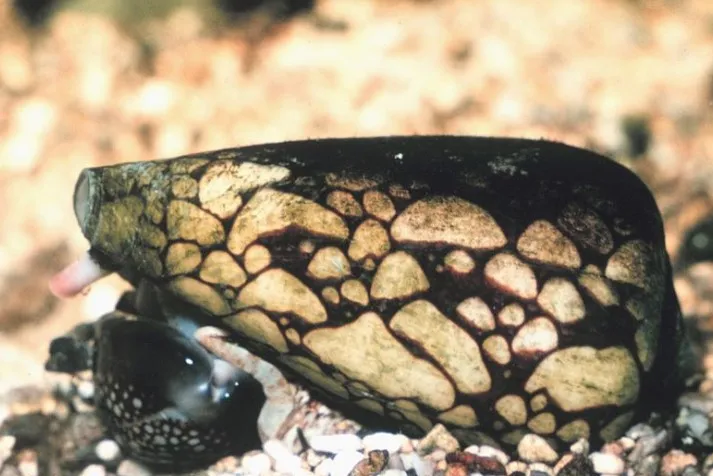
2. Marbled Cone Snail

| Scientific Name | Conus marmoreus |
| Size | Up to 15 cm |
| Habitat | Temperate to tropical oceans |
| Location | Okinawa, Japan, southern tip of India, southeast to New Caledonia and Samoa |
| Danger Level | Highly poisonous |
| Number of Deaths in a year | Estimated around 10 deaths per year |
These snails are indeed gorgeous, but they are very dangerous. A single drop of this snail’s venom is capable of killing 20 adult people! While some animals’ poison is more lethal, none can do as much damage with as little.
A cone snail sting can cause tingling, swelling, numbness, and excruciating agony. Symptoms in severe cases include respiratory paralysis, visual impairment, and muscle paralysis.
The idea that you may feel the effects immediately but that they may take days to manifest does not set my mind at ease!
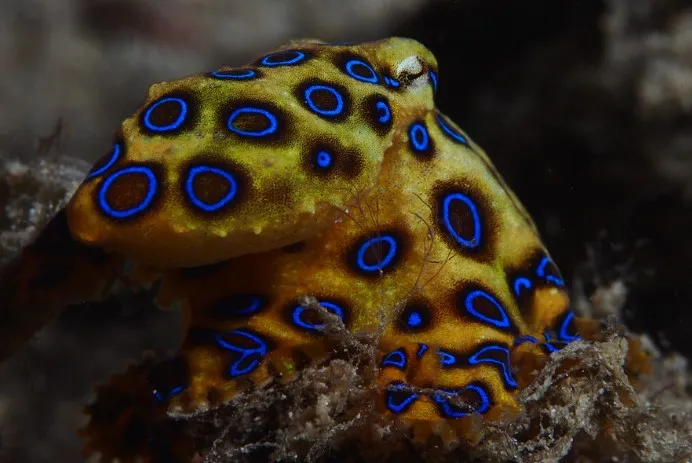
3. Blue-Ringed Octopus

| Scientific Name | Hapalochlaena lunulata |
| Size | Up to 8 inches (20 cm) in length |
| Habitat | Shallow coral reefs and tide pools |
| Location | Found in the Pacific and Indian Oceans, including Australia, Japan, and the Philippines |
| Danger Level | Highly poisonous, potentially lethal |
| Number of Deaths in a year | Estimated around 4-7 deaths per year |
One of the four species of extremely venomous blue-ringed octopuses in the Octopodidae family is the greater blue-ringed octopus. This particular species is one of the most poisonous animals under the sea.
As a warning signal, the octopus normally flashes its iridescent rings for about a third of a second.
To see if blue-ringed octopuses might generate their own blue iridescence, scientists immersed octopus samples in a variety of substances known to impact chromatophores and iridophores. Later, it was found out that none of the chemicals utilized had any effect on the octopuses’ capacity to make blue rings. Isn’t it a wonder?
4. Stonefish

| Scientific Name | Synanceia spp. |
| Size | Up to 30 cm (11.8 in) |
| Habitat | Coral reefs, rocky areas |
| Location | The Indo-Pacific region, Australia, Japan, and Caribbean |
| Danger Level | Extremely poisonous |
| Number of Deaths in a year | Estimated around 3-5 deaths per year |
Synanceia poison contains verrucotoxin (VTX), a proteinaceous toxin that affects Ca2+ channel function via the -adrenoceptor-cAMP-PKA pathway.
In humans, stings can cause severe pain, respiratory weakness, cardiovascular damage, convulsions, and paralysis and can even result in death. Stonefish stings are exceedingly painful and can be fatal, hence, it is among the top most poisonous animals under the sea.
The two most commonly advised therapies are heat therapy to the affected area and antivenom. Heated water of at least 45 °C (113 °F) administered to the damaged area denatures stonefish poison while causing minimal discomfort to the victim.
5. Irukandji Jellyfish
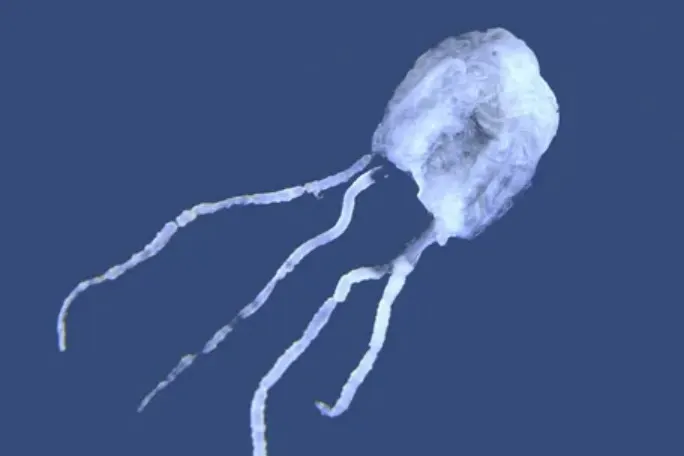
| Scientific Name | Carukia barnesi |
| Size | Up to 2.5 cm in bell diameter |
| Habitat | Tropical waters |
| Location | Northern Australia, Thailand, New Guinea, New Zealand, Malaysia, Philippines, Vietnam, and some Pacific islands |
| Danger Level | Extremely dangerous |
| Number of Deaths in a year | Estimated around 1-2 |
Unlike most jellyfish, which only have stingers on their tentacles, the Irukandji possesses stingers on both sides of its bell. Biologists have yet to determine the function of this distinct feature.
According to the theory, the characteristic aids the jellyfish in catching its meal of small fish. Irukandji jellyfish may inject poison and fire stingers from the tips of their tentacles.
The stings of the Irukandji jellyfish are so painful that they can induce fatal brain haemorrhages and send 50-100 individuals to the hospital.
6. Grey Side Gilled Sea Slug
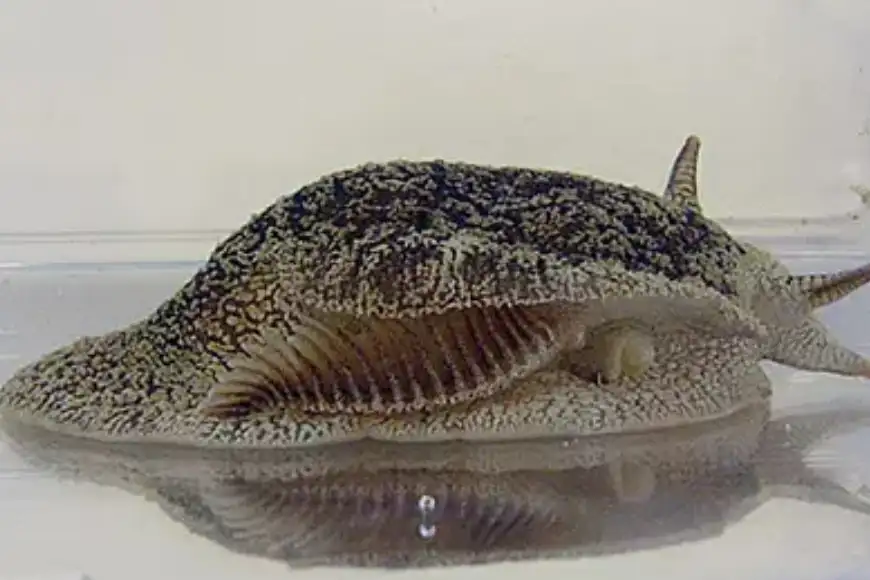

| Scientific Name | Pleurobranchaea maculata |
| Size | up to 10 cm |
| Habitat | a wide range of marine coastal habitats including rocky coastline |
| Location | New Zealand, south eastern Australia, Japan, and Sri Lanka |
| Danger Level | Highly toxic |
| Number of Deaths in a year | Death of several dogs per year |
Grey Side Gilled Sea Slug is a species of brown sea slug that is highly poisonous in nature. These slugs contain slugs contained tetrodotoxin (TTX), a potent neurotoxin with no known antidote that can kill humans. Every year, many dogs die due to Grey Side Gilled Sea Slug on Auckland beaches.
7. Pufferfish
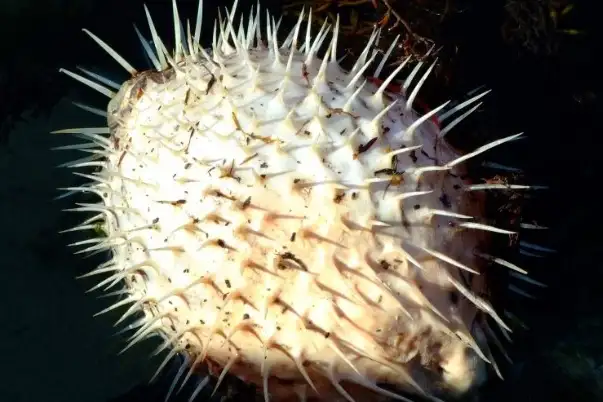

| Family | Tetraodontidae |
| Size | 3 inches to 2 feet |
| Habitat | Tropical and subtropical waters |
| Location | Northern and Southern US |
| Danger Level | Extremely dangerous |
| Number of Deaths in a year | 1-2 deaths on average |
They are physically similar to porcupinefish, which have enormous exterior spines (unlike the thinner, hidden spines of the Tetraodontidae, which are only visible when the fish have puffed up).
The scientific name relates to the four massive teeth fused into an upper and lower plate, which are employed to shatter the hard shells of their native prey, crustaceans and mollusks.
The majority of pufferfish species are deadly, and some are among the world’s most dangerous vertebrates as well as among the most poisonous animals under the sea.
8. Lionfish
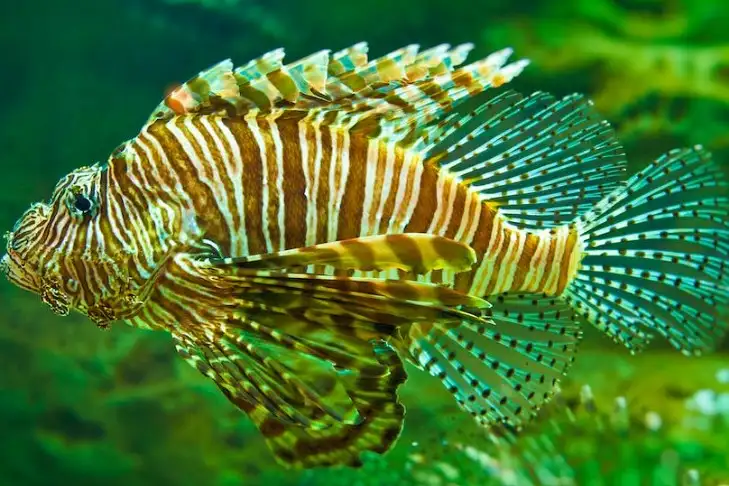

| Scientific Name | Pterois volitans |
| Size | Between 12 to 15 inches |
| Habitat | Coral reefs, rocky crevices, and mangroves |
| Location | Native to the Indo-Pacific but invasive in the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico |
| Danger Level | High |
| Number of Deaths in a year | 1-2 deaths on average |
Lionfish are noted for having poisonous fin rays, which make them dangerous to both other marine species and humans.
Pterois poison was found to have negative inotropic and chronotropic effects in both frog and clam hearts, as well as a depressed effect on rabbit blood pressure. These findings are assumed to be the outcome of nitric oxide production.
Hence, this species can produce systemic symptoms in humans, such as pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, headache, numbness, paresthesia, diarrhoea, sweating, transient limb paralysis, respiratory insufficiency, heart failure, convulsions, and even death.
Fatalities are more prevalent in infants, the elderly, and people who are allergic to the poison. Tell us why it appears among the most poisonous animals under the sea!
9. Portuguese man o’ war
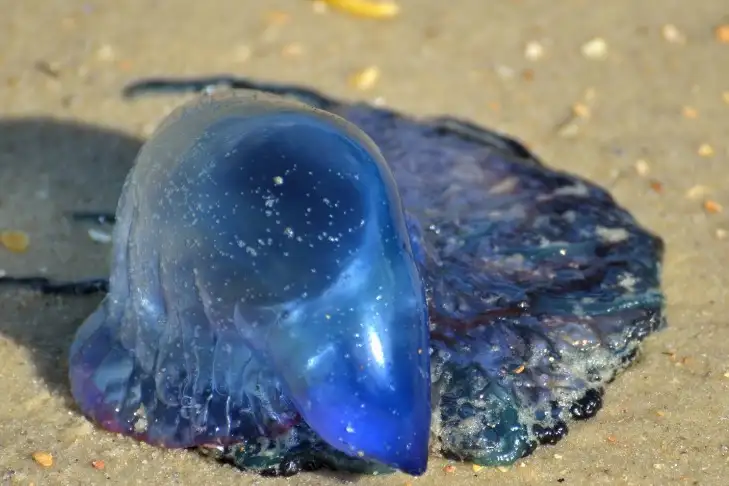

| Scientific Name | Physalia physalis |
| Size | Up to 30 cm long tentacles, with a float that can be up to 15 cm long. |
| Habitat | Ocean surface waters |
| Location | Tropical and subtropical waters around the world, including the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans |
| Danger Level | High |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
The Portuguese man o’ war is a prominent member of the neuston, a community of creatures living on the ocean’s surface. It has several poisonous tiny nematocysts that inflict a painful sting strong enough to kill fish and has been reported to kill humans on occasion.
Although it appears to be a jellyfish, the Portuguese man of war is actually a siphonophore. It, like all siphonophores, is a colonial organism composed of many smaller units known as zooids.
10. Nudibranch

| Scientific Name | Nudibranchia |
| Size | 2 cm to 60 cm |
| Habitat | Marine, usually benthic |
| Location | Found in oceans worldwide |
| Danger Level | High |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
Nudibranchs have a wide range of body forms, but because they are opisthobranchs, unlike the majority of other gastropods, they appear to be bilaterally symmetrical externally (but not internally) due to secondary detorsion.
The male and female genital openings are on the right side of the body in all nudibranchs, indicating their asymmetrical ancestry. The mantle cavity is absent.
Several species have cerata, or poisonous appendages, on their flanks to ward off predators. Many also have a straightforward gut and a radulated mouth.
11. Flamboyant Cuttlefish

| Scientific Name | Metasepia pfefferi |
| Size | Up to 8cm in length |
| Habitat | Shallow tropical reef environments |
| Location | Indo-Pacific region |
| Danger Level | Moderate to humans |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
During the day, the species is active and has been recorded hunting fish and crabs. It stalks its prey using intricate and varied camouflage. This species’ usual base color is dark brown.
Those who have been disturbed or attacked rapidly change color to a pattern of black, dark brown, and white with yellow patches around the mantle, arms, and eyes. To fend off potential predators, the arm tips are frequently painted bright red.
12. Greater Soapfish
| Scientific Name | Rypticus saponaceus |
| Size | Up to 61 cm (24 in) |
| Habitat | Coral reefs, rocky areas, and sandy bottoms |
| Location | Western Atlantic: from Florida to Brazil |
| Danger Level | Moderate to humans |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
A few morphological characteristics, such as the absence of anal fin spines, separate the genus from the remainder of the Serranidae.
It also only has two to four dorsal fin spines, whereas other serranids have more. The lower jaw protrudes, and the mouth is big.
The color varies, but a brown stripe runs from the mouth to the front of the dorsal fin in most cases.
13. Smooth Trunkfish

| Scientific Name | Lactophrys triqueter |
| Size | Up to 12 inches |
| Habitat | Coral reefs and rocky areas |
| Location | Western Atlantic Ocean |
| Danger Level | Moderate to humans |
| Number of Deaths in a year | Around 2 on average |
The smooth trunkfish is typically solitary; however, it does occasionally congregate in small groups. It expels a jet of water from its protuberant lips, which disturbs the sandy seabed and reveals any shallowly buried benthic creatures.
Little mollusks, polychaete worms, acorn worms, peanut worms, tiny crustaceans, sponges, and tunicates are among its favorite foods.
Care is advised, however, because it creates a poisonous chemical, ostracitoxin, in skin mucous secretions.
14. Yellowtail Amberjack
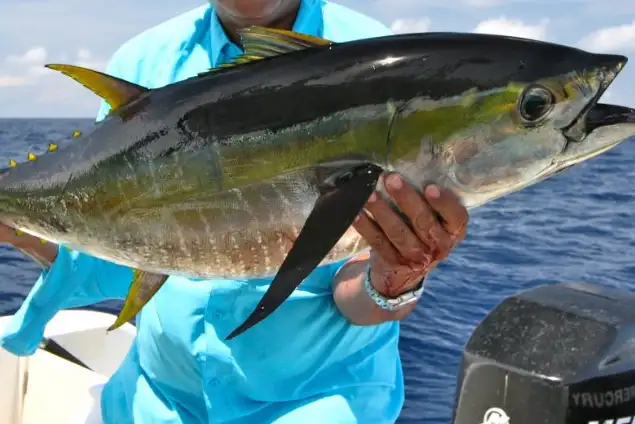

| Scientific Name | Seriola lalandi |
| Size | Up to 4 feet (1.2 m) |
| Habitat | Shallow and deep waters |
| Location | Pacific and Indian Oceans, Southern Ocean |
| Danger Level | Moderate |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
They thrive on coastal reefs and sandy environments, sometimes reaching estuaries. They have been collected at depths of nearly 300 meters.
In shoals of several hundred fish, 7-kg juveniles have been seen. Larger fish are found around deep reefs and offshore islands.
15. Smooth Toadfish
| Scientific Name | Lagocephalus laevigatus |
| Size | Up to 30 cm (12 in) |
| Habitat | Shallow waters, sandy or rocky bottoms |
| Location | Eastern Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea |
| Danger Level | Poisonous, extremely deadly |
| Number of Deaths in a year | Around 3 in Average |
The smooth toadfish has a small mouth and chin. The round eyes are adnate (unable to rotate), with their upper border level with the back profile and their lower border much above the mouth.
The nasal organs are two tiny papillae in front of the eyes. The fish’s back apertures are closed by flaps on the walls closest to its midline.
16. Xanthid Crab
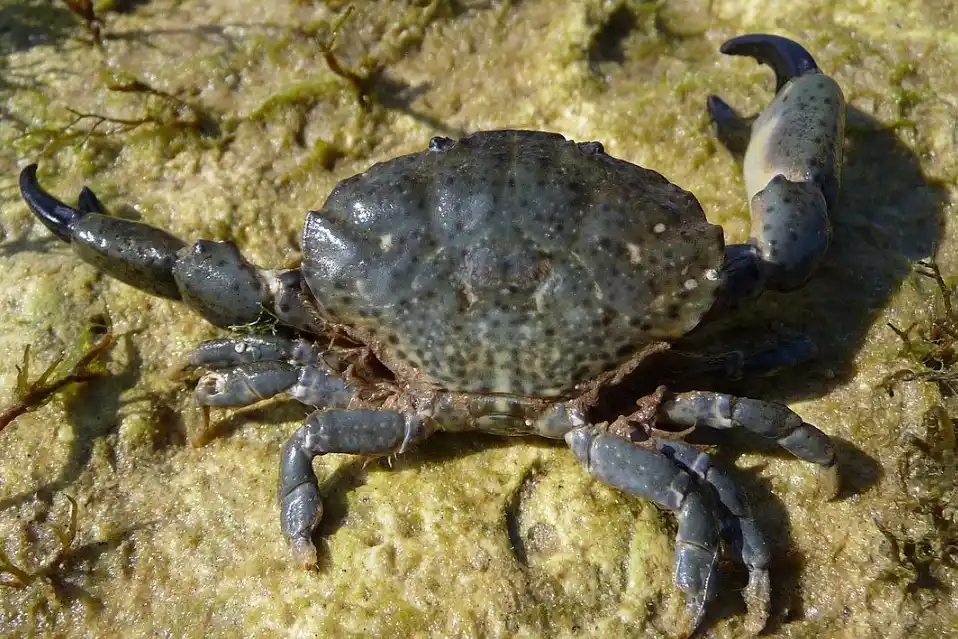

| Scientific Name | Xanthidae spp. |
| Size | 1-3 inches |
| Habitat | Saltwater |
| Location | USA, Singapore |
| Danger Level | Highly Poisonous |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
The highly toxic xanthid crabs are frequently vividly colored and carry toxins that cannot be eliminated by cooking and for which there is no known cure.
The toxins, which are related to those generated by puffer fish like tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin, may be created by bacteria of the genus Vibrio that coexist with crabs in a symbiotic relationship.
17. Giant Moray Eel
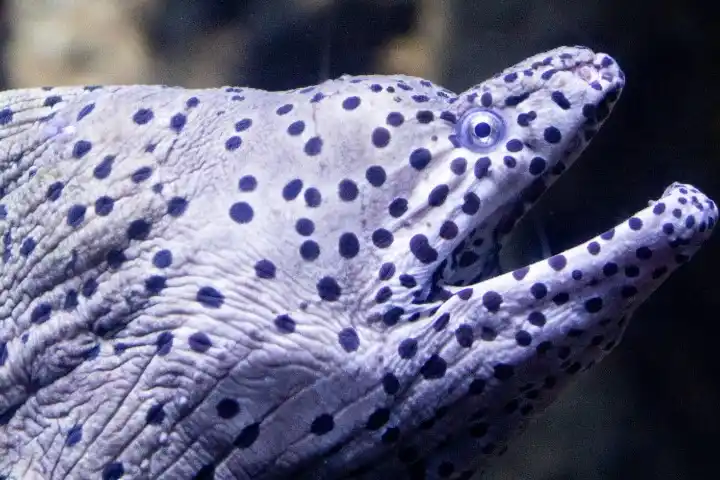

| Scientific Name | Gymnothorax javanicus |
| Size | Up to 3 meters |
| Habitat | Coral reefs, rocky crevices |
| Location | The Indo-Pacific region, Red Sea, East Africa, Australia, Japan |
| Danger Level | High |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
It is the largest moray eel in terms of body mass, although the slender giant moray is the biggest in terms of body length. The enormous moray hunts its victim within the reef at night and consumes meat.
It has a reputation for cooperating in hunting with roaming coral groupers (Plectropomus pessuliferus).
These two fish species hunt cooperatively: The grouper will consume the prey that the eel chases up and out of the reef as it hunts there.
Similar to how a grouper foraging over a reef may induce prey to try to find cover there, where a moray might ambush them.
18. Striped Pyjama Squid
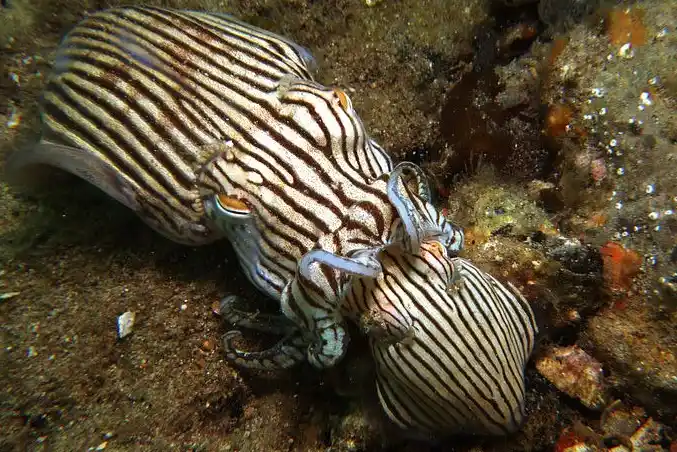

| Scientific Name | Sepioloidea lineolata |
| Size | Up to 3 cm in length |
| Habitat | Benthic (bottom-dwelling) in shallow waters |
| Location | The Indo-Pacific region, from the east coast of Africa to Australia and Japan |
| Danger Level | Moderate |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
The striped pyjama squid may conceal itself by altering its appearance because it is a non-nautiloid cephalopod. When it is attacked or has to blend in with its surroundings, the squid will turn a dark brown or purple color.
Eight arms and two feeding tentacles are features of the Sepioloidea lineolata. It is tiny and has a rounded shell.
Moreover, Sepioloidea lineolata have glands beneath their bodies that can release a toxic slime once a predator attacks the squid. Many different proteins and poisons are present in the squid’s slime making it one of the most poisonous animals under the sea.
19. Sea Cucumber

| Scientific Name | Holothuroidea |
| Size | Varies, up to 3 feet |
| Habitat | Marine, found in all oceans |
| Location | Worldwide, in both shallow and deep waters |
| Danger Level | Low Toxic |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
Because of the toxins they contain, particularly holothurin, and because of their frequently impressive protective mechanisms, sea cucumbers are frequently overlooked by the majority of marine predators. It must not be taken lightly as it makes in the list of most poisonous animals under the sea.
Although they are not affected by their toxins, they are nonetheless prey for some highly specialized predators, such as the large mollusks Tonna galea and Tonna perdix, which paralyze them with a potent poison before consuming them whole.
20. Ocean Sunfish

| Scientific Name | Mola mola |
| Size | Up to 10 feet (3.3 m) long |
| Habitat | Open ocean near the surface |
| Location | Found in tropical and temperate oceans worldwide |
| Danger Level | Low |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
Ocean sunfish are foraging predators who eat a range of foods, but their favorite target is jellyfish.
Jellyfishes are almost entirely composed of water and are deficient in calories/nutrients. Hence a fish as huge as the ocean sunfish must consume a significant number of jellyfish to maintain its weight.
They have an incredibly fast growth rate and can gain hundreds of pounds in a year, so these jellyfish experts are constantly on the lookout. Though, they are not the most poisonous animals under the sea, they are still toxic to cause harsh symptoms.
Adults are too huge to be threatened by any but the largest potential predators; however, sea lions, killer whales, and large sharks devour medium-sized individuals.
21. Porcupinefish

| Scientific Name | Diodon holocanthus |
| Size | Up to 50 cm (20 in) |
| Habitat | Tropical and subtropical waters worldwide |
| Location | Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific ocean |
| Danger Level | Low |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
Porcupinefish may inflate their bodies by eating water or air, making them rounder. Its increase in size (nearly doubling vertically) limits prospective predators to species with much larger mouths.
Sharp spines that spread outwards when the fish is expanded give a second protection mechanism. Several species are dangerous because they contain tetrodotoxin in their internal organs like the ovaries and liver. This explains why they are one of the most poisonous animals under the sea.
Their poison has a potency of at least 1200 times that of cyanide. Many species of bacteria found in the fish’s food manufacture the poison.
22. Grouper

| Scientific Name | Epinephelus spp. |
| Size | 30-40 inches |
| Habitat | Coral reefs and rocky bottoms |
| Location | Tropical and subtropical oceans, Africa, Central America, North America, and South America |
| Danger Level | Low to moderate (depending on species) |
| Number of Deaths in a year | No information |
The huge Goliath grouper, the largest grouper, can grow to be 8 feet long and weigh over 800 pounds. The Coney is the smallest, growing to approximately a foot in length and weighing about a pound.
Carnivores and groupers frequently consume smaller fish, such as other groupers, and crustaceans, such as shrimp and lobsters. Little sea turtles are eaten by large groupers, such as the Goliath grouper.
Sharks, king mackerels, and moray eels eat groupers. But the only predator that can consistently handle a fish the size of an adult Goliath grouper is a human.
Conclusion
Here we conclude the list of most poisonous animals under the sea, some of which can be fatal to humans.
Each of these creatures, from the tiny but deadly dart frog to the terrifying Blue-ringed octopus, has its own arsenal of toxins. Plus, their defense mechanisms are also weapons to inflict serious harm or even kill its prey.
Being aware of and preparing for the potential dangers posed by these creatures is essential. Do not interact with or eat any of these species. And as caution, rush to the hospital if you think you may have been poisoned.
From a safe distance, these creatures might be interesting to watch. But don’t put your guard down as they can pose a serious risk to human life and health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the most poisonous animal in the sea?
Ans. Synanceia verrucosa, the reef stonefish or simply stonefish is the most venomous fish in the world according to Wikipedia.
Q2. What is the most dangerous predator in the sea?
Ans. As the apex predators in the marine environment, killer whales have no natural predators. Because of their intimidation, it is therefore considered to be the most dangerous predator in the sea.
Q3. What is the world’s most poisonous animal?
Ans. The world’s most venomous animal is the box jellyfish. Minutes after a sting, one may pass away.
Q4. What are the top 5 deadliest fish?
Ans. The great white shark, reef stonefish, killer whale, the lionfish, and puffer fish are among the world’s top deadliest fish.
Q5. What is the 2nd most venomous fish?
Ans. The puffer fish is the 2nd most venomous fish on earth.
Q6. What fish are spiny poisonous?
Ans. This is the Red Lionfish. Their venomous fin spines are well known for their ability to cause painful, albeit infrequently fatal, puncture wounds.
Q7. Are piranhas poisonous?
Ans. To dispel the myth, neither the piranha flesh or its bite is poisonous.
References:
- The Most Poisonous & Dangerous Marine Sea Creatures by scuba
- 16 Beautiful but Deadly Poisonous Frogs by treehugger
- Wikipedia
- Sciencefocus.com
- Britannica.com
- A-Z animals
Also Read:

Anjali Prasad, a B. Pharm. graduate who works as a content writer for HowItSee, is based in Delhi. Except for her, not many people take the typical road from healthcare to writing. Her love of writing stemmed from her involvement in the college literature society and her early journaling at the age of 7. Hence, the love of learning and the spirit of exploration are what drew her to this career. You can find her on common social media like Instagram.
